Cloud computing has been established for a long time. The advantages over the classic supply of IT services in the own data center are becoming increasingly dominant. The question for companies is therefore not whether they should use cloud computing, but what type of cloud model or which provider they choose.
The public cloud is very attractive for companies because of its direct availability. A public cloud is an IT service delivered by a provider via the public Internet. Users do not need to install or operate their own hardware. They share the public cloud provider’s infrastructure with other companies. However, data and applications are usually completely separated from each other.
The so-called Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud are also in high demand. With the Hybrid Cloud, the advantages of public and private clouds can be combined in a common cloud environment. The Multi Cloud creates a cloud environment consisting of several public clouds.
In the following article, we would like to give you an understanding of the Public Cloud. We explain what a public cloud is, what advantages it offers, and where its limits are. Furthermore, we will dispel any misconceptions: A public cloud is less secure than a private cloud. A few use cases are intended to illustrate the sensible use of the public cloud.
The Public Cloud in Detail
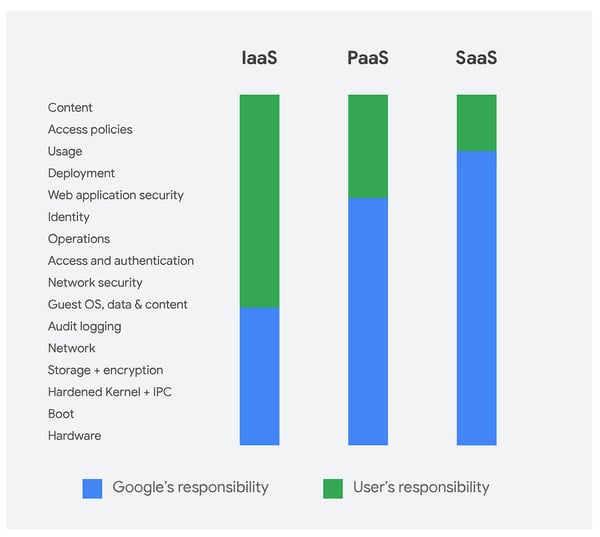
Regardless of whether private or public cloud, cloud computing distinguishes between these three basic service models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
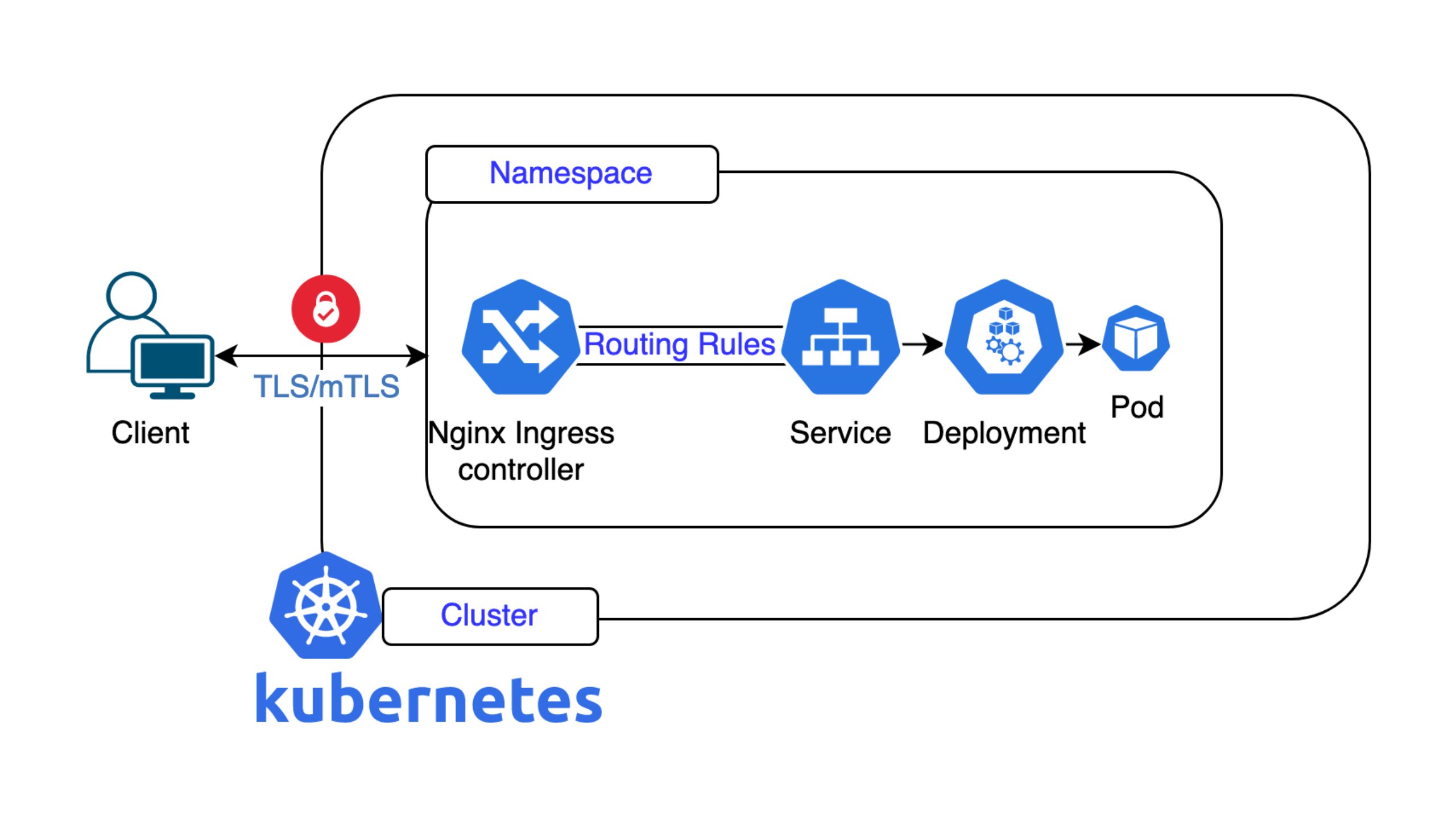
While IaaS provides customers with virtualized IT infrastructure such as computing power, networks, or storage space, PaaS provides runtime and programming environments for developing or operating their own applications. An example of an IaaS service is the nine cloud servers. They provide customers with computing power, storage space, and network connectivity. With the Managed Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) from nine, you get an offering that can be ranked under PaaS. SaaS makes applications or software available over the Internet. Typical examples are Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and Forms for the collaborative creation of text documents, tables, presentations, and questionnaires.
The services of a public cloud are available to customers via the public Internet. Companies select the services they need themselves and order them from their cloud provider. It is not necessary to install and operate their own IT infrastructure for these services. The provider operates and manages the hardware and software (depending on the service model) in its data centers. For example, employees of the provider maintain servers, operating systems, and software, apply updates and patches, monitor the performance of the computers, secure the systems against hackers or unauthorized access and ensure high availability through redundancy. If a customer needs more performance, he can flexibly expand the services via web-based self-service user interfaces. The services are easily scalable and adapt to the needs of the company. The services used are generally billed on a usage basis. Customers of a public cloud only pay for the services and resources they have actually ordered and used.
Difference between Public Cloud and Private Cloud
In contrast to a public cloud, the services of a private cloud are not available to the general public, but only exclusively to an individual company. A private cloud is either operated by the company itself or has outsourced its operation to a service provider. Hardware and software are either installed in the company’s own data center or in the data center of the service provider. The private cloud allows maximum control over the resources used and permits individual applications and services. The services are accessible either via the company network or via the Internet and virtual private networks (VPNs). A private cloud may become necessary if, for example, strict legal data protection regulations or security requirements prohibit outsourcing data and applications to an external service provider, or if very specific services are required.
What are Multi Cloud and Hybrid Cloud?
The two cloud models Multi Cloud and Hybrid Cloud play an increasingly important role. The Hybrid Cloud combines the services of a private and a public cloud. A joint cloud environment is created, whose services are obtained as required from a public or a private cloud. This allows the best of both worlds to be combined. The nine cloud navigators also support hybrid setups thanks to two of their own redundant data centers and the partnership with Google Cloud. Thanks to that nine can optimally support you in operating a hybrid setup.
A Multicloud is a combination of several public clouds from different providers. The provider with the best cloud offer can be selected for the services required. The Multicloud reduces dependency on individual providers and provides more redundancy.
Misunderstanding security
One of the biggest misconceptions about the public cloud is the security of the public cloud. It is claimed that a private cloud is automatically more secure than a public cloud. Looking at the details, this prejudice is difficult to prove. Although a private cloud is not available to the general public on the Internet, it is still connected to the Internet. Hackers can also find and attack a private cloud. Companies have complete data sovereignty in a private cloud but are responsible for the security of their cloud environment. Monitoring the private cloud, applying security patches, and fending off attacks requires a great deal of effort and expertise. If a company protects the private cloud insufficiently or lacks the necessary security know-how, it is vulnerable to attacks.
In terms of data protection, the public cloud offers a high level of security that can compete with a private cloud in many areas. Many public cloud providers give their customers the option of choosing the cloud location for service delivery. In addition, there is the option of comprehensive data encryption. Strict data protection and compliance requirements can be implemented. Certifications play a major role here, which is standard for the public cloud, whereas in the private cloud they relate only to the data center and not to the infrastructure brought by the customer.
Public Cloud: Typical use cases for companies
After so much theory, let’s look at some use cases. Below are three examples of typical use cases of a public cloud:
E-Commerce applications with dynamic resource requirements
Suppose your company is in the e-commerce business and runs an online shop with sales that are highly seasonal. Of course, you always want to offer your customers the same user and shopping experience. During the Christmas business, for example, your e-commerce systems should not have longer response times. If you operate the servers for your applications yourself, you must dimension them so that they are designed for peak loads. This means that the servers are only moderately loaded for most of the year. They waste resources and work inefficiently. When you use a public cloud, you can scale performance as needed. The services are elastic and can be easily expanded temporarily for the Christmas season. You only pay for the capacities actually booked and, compared with an oversized in-house IT infrastructure, significantly reduce your costs.
As a startup being immediately available worldwide
For the success of a start-up, it is essential how quickly the company with its innovative business idea is available on the market (short time-to-market). However, a start-up in particular lacks the resources and an existing IT environment. There is simply no time and money to invest in hardware and software and to build up their own IT infrastructure. The public cloud offers a way out. The services of the public cloud are available worldwide immediately after booking. Globally distributed data centers ensure almost the same response times and performance in every corner of the world. The start-up company’s employees can take care of the further development of the business model without having to concern themselves with the operation or maintenance of the IT systems. This concentration on the core business and the demand-oriented provision of the required IT services by the public cloud provider increases the startup’s chances of success.
Provide redundancies for critical services
Another use case is the availability of redundancies for critical services. A company’s business processes often depend on a few applications or IT systems. A failure of a single server can quickly bring the entire company to shut down and cause immense loss of revenue. Providing redundant systems costs a lot of money and causes effort. In a public cloud, a second infrastructure can be provided, which can be activated in an emergency until the disaster recovery is complete and the original systems can be taken over again.
The advantages of the Public Cloud
- no investments in own IT infrastructure necessary
- transparent, usage-dependent costs
- Minimum effort to operate and manage certain services – the provider installs, operates, maintains and monitors the hardware and software to deliver most services
- Easy scaling and configuration of services via web-based user interfaces or APIs
- fast availability of the booked services
- Providers ensure high availability and security of applications, data, and services
- Providers of a public cloud have a great deal of know-how for the secure operation of their IT – the most modern security concepts are implemented with corresponding certifications
- access to the cloud services is possible everywhere via the public Internet
The Limits of the Public Cloud
A public cloud reaches its (local) limits when data requiring special protection, such as medical data, financial data, or legal data, are to be stored and processed. The public cloud is usually operated in certain regions, usually limited by national borders. This means that the public cloud can only be used within a certain area to which certain local laws and legal judgments apply. As a customer, it is important here to check with the cloud provider to ensure that they comply with local laws and other regulations (financial, medical, etc.).
Since several customers share the same cloud resources, it cannot always be 100% ruled out that performance or availability will influence each other. It is possible that not all the services you need are available. However, this should be seen in relation to the location and the possibilities of the respective public cloud: Since the public cloud generally has a larger scope and more technical resources, the availability of resources can be regarded as at least as good as in the private cloud.
The nine cloud navigators support you on your way to the public cloud
It is not always easy to select the right cloud for the individual requirements of a company. Private and public clouds offer specific advantages and disadvantages that need to be considered. In addition, with the Hybrid Cloud and the Multi Cloud, there are other cloud models that can represent suitable solutions depending on the applications to be implemented.
In many cases, however, there is no way around the public cloud. It is a must for companies that need professional IT services but want to concentrate on their core business and do not want to waste resources on operating their own IT infrastructures.
The nine cloud navigators help you on your way to the cloud. They are there to help you choose the right cloud environment – whether private cloud, hybrid cloud, public cloud, or the respective managed version. Together with you, we will find the optimal solution.
Our cloud experts will be happy to answer your questions or introduce you to our managed public cloud solution based on the Google Kubernetes Engine.